Vst Waves How To Unistall Specific Plugins
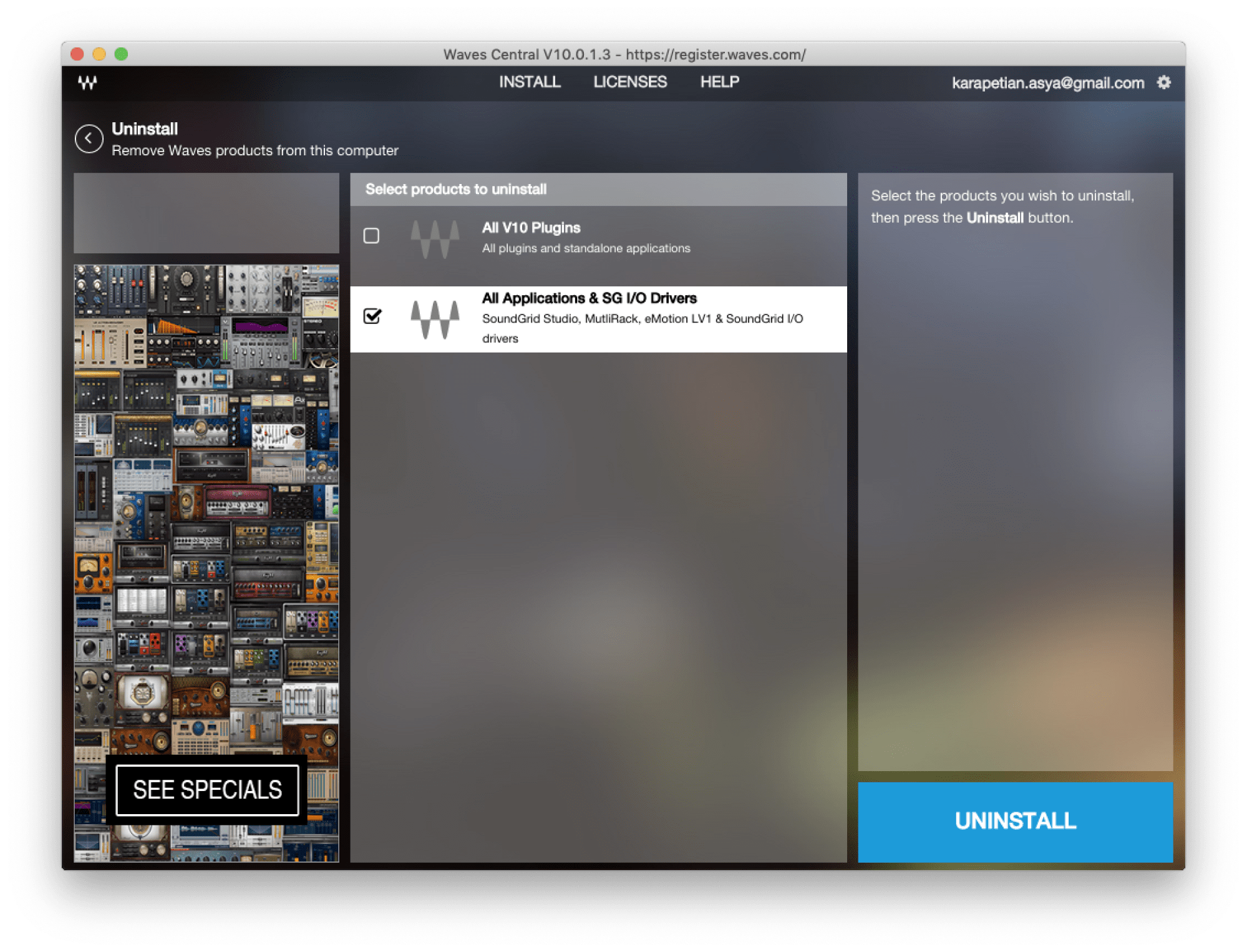
For instance, you can only uninstall all your Waves V12 plugins at once—or all your Waves V10 plugins at once. Individual plugins must be removed manually, as described below. Waves applications (such as SuperRack or eMotion LV1) and Waves SoundGrid I/O drivers can only be uninstalled together as one. Uninstall via Waves Central. I have Waves 7, didn't uninstall before installing Waves 8. Pro Tools kept asking for the location of the Waves 7 Plug-ins. Pressing the SHIFT during PT Boot let me deselect evoking the Waves 7 plug-ins, but Pro Tools STILL wanted to know where they were.
- Vst Waves How To Uninstall Specific Plugins Plugin
- Vst Waves How To Uninstall Specific Plugins Minecraft
Finding the essential VST plugins to use in your digital audio workstation is important if want to attain any success in your producing, recording and mixing.
While your DAW provides the canvas where you form your musical masterpieces, the plugins are the tools which allow your masterworks to take shape.
So in this article we’ll go over what are some of the essential types of plugins you’d need to pay attention to.Adobe package for mac and android.
Some other helpful posts:
If you’ve been producing for at least a little while, you’ll know that it can be overwhelming to decide on the right plugins to use.
It’s like a beginner carpenter looking at an expert toolshed. There are a plethora of tools available to you, but which one to use? And for what purpose?
The music production software world is saturated with software plugins. Every week there seems to be a new plugin or plugin update that offers some new or enhanced features. It can get overwhelming, either with excitement or confusion, when deciding on what plugins to use.
Does this mean that the plugins that you find in music production online stores are unnecessary? No, but you do need to understand what VST plugins are, and also very importantly, what it is you’re trying to achieve in your music in the first place. Then you can decide on what other plugins want to use in your music making and recording.
If you start from the simple basics, you’re sure to advance according to your needs.
The Essential Plugins You Should Use
If you don’t know what plugins to choose from, quite likely you will end up wasting a lot of money and hard drive space on trying out unnecessary plugin software.
It is best to stick the basics of what you need. From the basics, you should seek to achieve sonic mastery by becoming competent in the essential tools.
When you break it down, there are only a small portion of essential VST plugins that you need to handle the necessities of recording and editing any audio.
What are the essential plugins?
All the essential plugins you need will come in just four general categories:
- Virtual Instrument Plugins – also called VSTi
- Effects Plugins – sometimes referred to as Effects processors
- Dynamics Plugins – sometimes referred to as Dynamic processors
- Emulation Plugins
Of course, we’ll need to break it down and we’ll find that these two categories consist of subcategories. So let’s take a look at those.
Virtual Instrument Plugins
VSTi’s are plugins that emulate actual musical instruments. They come in a few different types:
- Samplers
- Softsynths
- Drum Machines
What these plugins do is emulate the sounds of a real live instrument in your digital audio workstation. You can “play” these virtual instruments using a midi controller/instrument, or you can write the notes into your piano roll using your mouse.
Sampler Plugins
A sampler takes samples of recorded sound and plays them back. These tend to require the largest amount of GB space in terms of size, simply because they require lots of audio files to be saved onto your system. These audio files are what will be retriggered for playback within your DAW, usually via MIDI controller.
A sample could be anything from a drum kick to a note on the piano. The high-quality ones record them at various “velocities” (soft or loud). Once you trigger a note within the VST from your MIDI controller or from your DAW’s piano roll, the sound sample will be reproduced.
Read: MIDI Controllers for Music Production
Softsynths
A soft synth takes up far less space, but will use up more CPU power.
Softsynths are software synthesizers (hence the name) that work just like your analogue synthesizers, employing various methods of audio synthesis to produce digital audio.
With a synthesizer, you can construct and create new sounds. Practically any sound you like can come from a synthesizer, you’d just have to first learn how to use the various parameters of a synth. Once you do, a whole entire world of sound design will be open up to your fingers and ears, with limitless possibilities and potential.
Drum Machines
Vst Waves How To Uninstall Specific Plugins Plugin
A drum machine VSTi is just as the name suggests. It is a drum emulation software that creates looped beats and grooves. They are usually more often used in the electronic music genres, like house, but can be utilized in other styles of music as well.
The basic function of a drum machine is to create groove beats and rhythms that can be looped over and over. A good drum machine VST will give you good sounds to use, whether synthesized or sampled. It will have the ability to alter the effects of those sounds using EQ and other effects. You should also be able to create multiple loops that you can trigger to play at various points in your track.
We have just covered the first broad category of plugins. Now we will take a look at the second category, the type of plugins that don’t (usually) make any sounds of their own, but will go a long way to enhancing the sound of your virtual instruments and audio recordings.
Effects Plugins
Linn drum vst plugin. Effects plugins are used to change or adjust the sound of the audio coming in and going out of your digital audio workstation.
Generally speaking, but not always, effects processors work in the “time domain,” meaning, they alter the way the sound is perceived or produced within time, to produce a desired effect.
They are essential plugins to have, if you want to get any satisfactory sound from your music. Examples of these are:
- Reverbs and Delays
- Choruses
- Flangers and Phasers
Reverbs and Delays
Reverbs and Delays adds an extra tail of sound to your audio. Reverbs are called upon to add more room and space to your sound, like the sound of singing or playing in a small room or a large theater. They can be very important for vocals, giving the singer presence in the mix. In the studio context, this usually means recording them “dry” and then using either a software or hardware reverb plugin to add the desired effect of space and room.
Some reverbs, like spring reverb plugins, act simply as an effect. They work by thickening a sound and providing more presence to drums, vocals, or guitars.
Delays are also called echoes because they produce an echoing feedback effect on a sound. Similar to reverb if you want to add space to your sounds.
Choruses
Choruses double or multiplies your audio signals to make it seem as if there are multiple instruments or voices being played back. Also a good effect for adding presence when you use it right.
Most likely, the DAW that you’re using has all of these plugins already. In many DAWs like Studio One, Pro Tools, Logic Pro, Reason or Ableton, the plugins that come with the software would already be enough to use. Especially if you’re just starting out, but even after you’re an advanced DAW user, you can still rely on the plugins that come with your DAW.
Flangers and Phasers
Flangers and Phasers give audio an unusual “wah-wah” effect to your audio. These are usually effective in cutting out some frequencies and allowing the instrument to sit well in a large mix. But you can also use it for the effects they provide.
Dynamic VST Plugins
Dynamic plugins are dynamic processors that alter the amplitude of the audio signal to provide desired results. This means, the will either boost or cut parts of or whole frequency sections of an audio signal to change the way it sounds, or otherwise change the way the signal’s loudness is perceived.
Some examples of dynamic processors are:
- Equalizers (or EQ for short)
- Filters
- Compressors and Limiters
EQs and Filters
Equalizers allow you to adjust the amplitude of specific or ranges of frequencies in your audio. That means, you can make the lower end (bass) louder or softer, narrow in on certain sounds you’d rather not hear, or boost, or reduce or increase very high sounds in your audio.
These plugins are essential when mixing vocals, or any other instruments, since they carve out spaces for each audio signal to occupy in a mix. That way, one’s fighting for space to be heard. You can find here some examples of professional third party EQs for vocals. Otherwise, the ones that came with your DAW should suffice if you’re just starting out.
Also, filters, another type of plugin, work like EQs, but they allow you to “filter out” entire ranges of frequencies. This can be a useful effect when combined with software automation within the DAW.
Compressors and Limiters
Compressors and limiters are essentially the same things. They both affect the perceived loudness of audio by reducing the volume of loud sounds in your music, or amplifying the quiet sounds. Doing this “compresses” the audio signal’s dynamic range to just a small difference between loudness and softness.
Limiters do the same things, except that it reduces the volume attack (transients) much faster, giving quieter sounds and frequencies the ability to amplify more, therefore increasing the perceived loudness.
There is also another kind of compressor called the “de-esser,” which is designed specifically for those frequencies where you have that “SSS” sound. This removes sibilance from vocals and also from instruments like hi-hats, guitar and bass slides.
Emulation Plugins
Because we work on digital audio files, there’s a tendency for music purely mixed on a DAW to lose that the sort of character that a great sounding mix would normally have.
In this case, you reach for an emulation plugin that, like the name says, “emulates” the sound of analog hardware studio devices.
Some of these plugins come in the form of equalizer or delay/reverb plugins that we mentioned above. But if you can use a plugin to add the sort of warmth that recording on a tape machine would provide.
Though not entirely “essential,” to some, these plugins are a must have, especially when you get into mixing and mastering music.
A similar plugin is also the harmonic exciter. While not an emulator, both these hardware and software variants provide that brilliance often necessary in a dry digital mix.
How many plugins do you need?
Vst Waves How To Uninstall Specific Plugins Minecraft
The best advice is to start with the very basics of each plugin type. If you keep your choices down to the bare essentials, and learn to use these plugins well to do all the things you need for your production, mixes, and recordings, you’ll have an easier time with keeping yourself from “plugin overload”.
Does this mean that every other plugin you find on the internet is going to be useless? No, maybe even the opposite, because starting with the basics, you have a solid framework of what you’d like from a plugin, and what works for you and your music.
Here’s the thing, if you don’t even know how to use a basic plugin to its full potential, you’ll get lost in all the other features that come with more advanced plugins with all its fancy bells and whistles.
Final thoughts
As you can see, these are just an essential set of VST plugins that you need to use. The plugins that were mentioned will be enough to do all that is required in your production or mix. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can move on to other advanced third-party stuff, or experiment with using a different type.
Naturally, each plugin comes with its own style and way of doing things, so you may find that you develop your own favourites over time.
In the end, continue to have fun. You can give yourself permission to play with your own plugins, and get some new plugins to try out. But as you do so, remember to keep things simple. There’is an acronym for that, actually: KISS – Keep It Simple, Stupid.
Introduction
Microsoft announced that it would offer Visual Studio Express free of charge forever. Though the Express version of Visual C++ (hereafter referred to as VC++) has some limitations, it’s still a great tool and it’s nice to see Microsoft taking some steps to support the developers writing software for their platform. This document will describe how to get VC++ installed and building VST plugins. It assumes that you have prior experience developing VST plugins, and are familiar with the structure and layout of the VST SDK.
If you are trying to write VST’s in a language other than C++, than this guide is not for you. There are lots of other frameworks out there for developing VST plugins in other languages (such as C#, Java, Ruby and Python, just to name a few).
This tutorial will walk you through the process of installing and configuring the tools you’ll need to build your own VST plugins with Visual Studio, and creating a simple VST plugin with optional support for a VSTGUI frontend. This guide only covers building VST 2.x plugins, as the VST3 SDK is not very widely supported yet. Note that Steinberg’s website is a bit confusing and it is easy to accidentally download the wrong version of the SDK, so double-check to make sure that you have the 2.4 SDK.
Download required packages
- Steinberg’s VST SDK, which requires you to make a free Steinberg Developer account.
- Microsoft’s Visual C++. This guide uses the 2010 Express edition, as it was the latest version at time of writing.
- Libpng and zlib (optional)
Install Visual C++
If you already have a working installation of VC++, you can skip this step. Otherwise, download VC++ and install it. The standard installation should be OK, but you can choose to perform a custom installation if you don’t want documentation or other stuff installed with it. Before installing VC++, you must remove any other versions of VC++ on your computer.
Next, download and install the Platform SDK, which will provide you with the standard header files and libraries you’ll need to build software. You may choose to install VC++ anywhere on your hard drive, but the default location is C:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual Studio 10.0.
Creating your project
Create a new project of type “Class Library”, which we’ll call YourProjectName. In the rest of this tutorial, whenever you see YourProjectName, replace that text with the actual name of your project.
In Visual Studio 9, you’d make a new project with the wizard found at File -> New -> Project. Select Visual C++ -> Win32 Console Application, and choose a directory for your project. When the wizard opens, press “Next” and select DLL as the Application Type. Also check the “Empty Project” box.
If you prefer not to start with an empty project, then you can remove all of the files that VC++ creates for you, but keep the resource.h and YourProjectName.rc files, and remove any references to these files (such as YourProjectName.ico being listed in the resource file).
Add Source Code to the Project
If you already have source code for your plugin, simply add it to the project. Otherwise, you need to create the following files:
- YourProjectName.cpp
- YourProjectName.h
- resource.h (Only needed if building a plugin GUI)
- YourProjectName.rc (Only needed if building a plugin GUI)
You will also need to add the files from the VST SDK, which includes everything under the vstsdk2.4/public.sdk/source/vst2.x and vstsdk2.4/pluginterfaces/vst2.x directories. I usually prefer to manually make groups for these directories and drag the files to the groups from Explorer, as dragging the entire “vstsdk2.4” directory to VS can cause it to choke when it tries to add a bunch of unused files to the project.
To start out with, the plugin’s entry point header file (YourProjectName.h) should look something like this:
The accompanying class definition (YourProjectName.cpp) should look something like this:
Note that your project won’t compile just yet, but be patient!
The above code samples are simply blank entry points which don’t do anything exciting. The VST SDK offers lots of methods which you can override in order to do things like setting parameters, receiving MIDI messages, and so on. These things are beyond the scope of this tutorial; if you don’t know what code to put inside of processReplacing, try checking out the “again” example distributed within the VST SDK in the public.sdk/samples/vst2.x/again folder.
You must also create a module definition file for your project, named YourProjectName.def. Usually this file is placed in the same directory as the VC++ project file, but you may place it somewhere else so long as this definition matches the Module Definition File settings in the Linker section of the project preferences. This is just a plain-text file which should contain the following text:
Configure build settings
Go to the project settings either by right clicking on the project in the solution explorer and then selecting “Properties”. Make the following changes to the project for all build configurations:
- General
- Character Set: Not Set
- Common Language Runtime Support: No Common Language Runtime Support
- C/C++
- General:
- Additional Include Directories:
- (or wherever you put the VST SDK)
- Your source code directory
- Any other directories which you may have header files stored in Global SDK directories, such as
- Additional Include Directories:
- Preprocessor:
- Preprocessor Definitions:
- For Debug builds you may also wish to add
- If you wish to use PNG graphics for a VSTGUI frontend, add
- To avoid lots of compiler nags and warnings, define
- In some cases, you may also need to define
- Code Generation:
- Runtime Library: Multi-threaded. Multi-threaded debug may be used for debug builds. This will build the VC++ common runtime library statically into your plugin, increasing its size by approximately 200Kb. If you choose to use the CRL as a dynamic library, then you must also distribute a copy of the CRL with your application, which complicates deployment and distribution.
- Precompiled Headers:
- Precompiled Header: Not Using Precompiled Headers. Yeah, this makes rebuilding a bit slower, but will avoid a bunch of weird errors as you are getting your project set up. Once you get the project building you can revisit this step.
- General:
- Linker
- General:
- Additional Library Directories: Add any other library directories which your project depends on.
- Input:
- Additional Dependencies (for Release builds):
- libcmt.lib
- uuid.lib
- shell32.lib
- ole32.lib
- gdi32.lib
- User32.lib
- advapi32.lib
- zlib.lib (only if you are building with a GUI)
- libpng.lib (only if you are building with a GUI)
- Additional Dependencies (for Debug builds):
- shell32.lib
- msvcrtd.lib
- ole32.lib
- gdi32.lib
- User32.lib
- advapi32.lib
- zlib.lib (only if you are building with a GUI)
- libpng.lib (only if you are building with a GUI)
- Ignore Specific Default Library (for Release builds):
- msvcrt.lib
- libc.lib
- msvcrtd.lib
- libcd.lib
- libcmtd.lib
- Ignore Specific Default Library (for Debug builds):
- libcmt.lib
- libcmtd.lib
- msvcrt.lib
- Module Definition File: YourProjectName.def
- Additional Dependencies (for Release builds):
- General:
Adding support for VSTGUI (optional)
Include VSTGUI support in your plugin, simply add the VSTGUI files into your project in addition to your own editor class. At a very minimum, these are:
- aeffguieditor.cpp
- vstcontrols.cpp
- vstgui.cpp
Adding support for PNG graphics (optional)
If you would like to use PNG’s in your plugin instead of BMP graphics, you will need to also build your own version of libpng and zlib. Download the source code for both libraries from the links given in the “Requirements” section of the document and place them in the same directory. There is a Visual Studio project for libpng which will also build zlib for you; it is located in the projectsvisualc71 directory. In order to get the projects to build correctly, you’ll need to rename the source code directories to simply “libpng” and “zlib”, removing the version numbers from the directory name.
When you open the project up, VC++ will run you through the project conversion wizard. Convert the project, and change the “Runtime Library” settings in both libpng and zlib to be Multi-Threaded, as described above. Unless this step is performed, the dependency on the CLR will be present in your project. Next, choose the LIB ASM Release or LIB Release build style and build the project; if you build the libraries as DLL’s, you will be unable to statically link them into your plugin. The project should build ok, but throw a few errors when attempting to run the pngtest files. You can ignore these problems, as the libraries will still be correctly compiled and can now be linked to your project.
Visual Studio doesn’t need to have the libraries within your actual project. Instead, place the libraries in a directory of your choosing and be sure to add this path to the list of “Additional Library Directories” in the Linker preferences for your project. You may choose to place the libraries in the same directory as the Microsoft Platform SDK stuff, but I personally prefer to keep them in a separate directory checked into version control. Also be sure to add references to libpng.lib and zlib.lib for your project in the “Additional Dependencies” section of your Linker preferences for the project.
The path must be relative to the location of the project file. Then, in resource.h, add the following preprocessor definitions:
Now you can use IDB_BITMAP1 (or any other name of your choosing) in your code when creating new CBitmap objects.
I have heard some reports of vstgui.cpp not compiling properly due to the missing symbol png_set_expand_gray_1_2_4_to_8. Changing png_set_gray_1_2_4_to_8 to png_set_expand_gray_1_2_4_to_8 in vstgui.cpp seems to fix this issue.
Final considerations
VC++ ships with an optimizing compiler, but sometimes the compiler will choke on certain files and optimization must be disabled. In particular, I have experienced this with Laurent de Soras’ FFTReal libraries, since they are written as template classes. In general, however, optimization is a good idea, as is “Eliminating Unreferenced Data” (in the linker settings). The “Whole Program Optimization” setting appears tempting, but usually results in dozens of build errors and problems, so it’s best to avoid this. Also, be sure to use the optimization features of this compiler and linker, as they can greatly boost runtime performance.
If you are developing on a multi-core machine, then you might need to disable parallel builds by setting the number of parallel builds to 1 under Tools -> Options -> Projects and Solutions -> Build and Run. In past verisons of VS, I noticed that the compiler does not always link projects in the order one would expect, which caused odd errors during linking about missing symbols. However, VS2010 users probably shouldn’t need worry about this setting.
Unresolved symbols when linking
Sometimes you may see errors like the following:
If you are getting errors in your build about missing symbols, make sure that you double- and triple-check the debug and release configurations for the library configuration above, since some of the libraries which are used in one build style are specifically excluded from the other. Also, when you close and re-open the project’s build properties, VS always “forgets” the last selected build style, so remember to check and set this appropriately.
Also, you should check to make sure that the Platform SDK was correctly installed on your system and that your project’s include and library paths are pointing to these directories.
Unresolved external symbols
If you are seeing errors like this:
Then this most likely means that the file which contains the given symbol is not correctly added to the VC++ solution.
Linking errors with symbols defined multiple times
This is undoubtedly one of the most frustrating problems which can occur when building a VST in VC++. If you are seeing error messages like this, then it most likely means there is some problem with your library configuration:
Most likely, the libcmt and msvcrt libraries are being included incorrectly in your build. Double-check the library list above, keeping in mind that the recommended configuration uses libcmt for release builds only, and msvcrtd for debug builds only.